Spring, the so-called beautiful season, has now begun: what to do with cacti and succulents? Should you take plants kept indoors outside during the winter? Remove covers or layers of non-woven fabric? Resume watering? Fertilize plants?
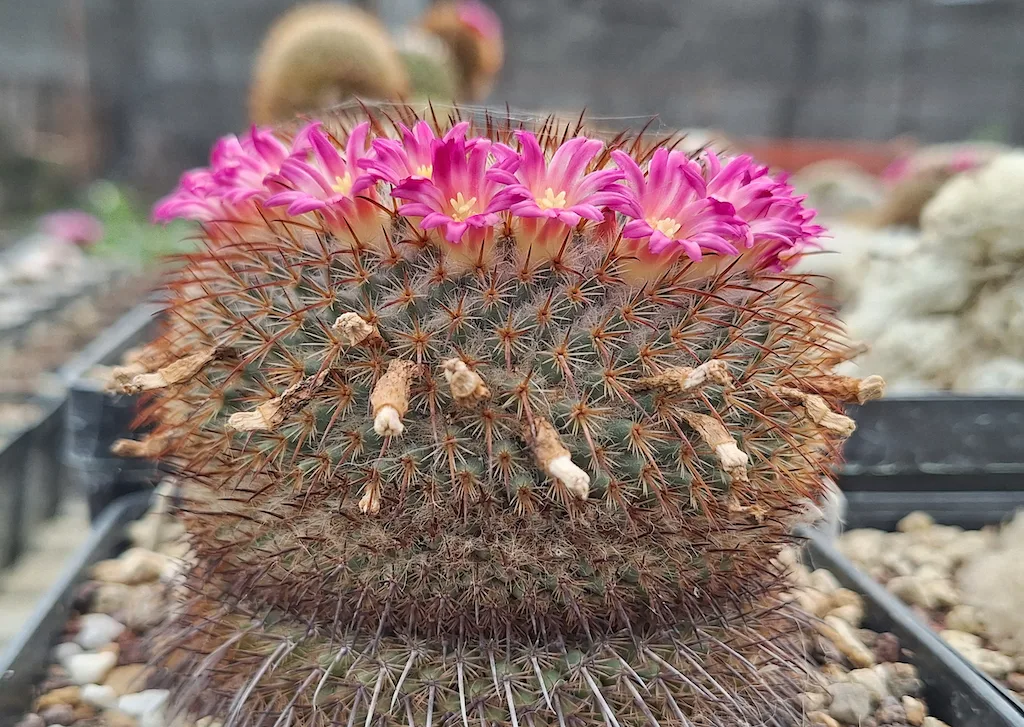
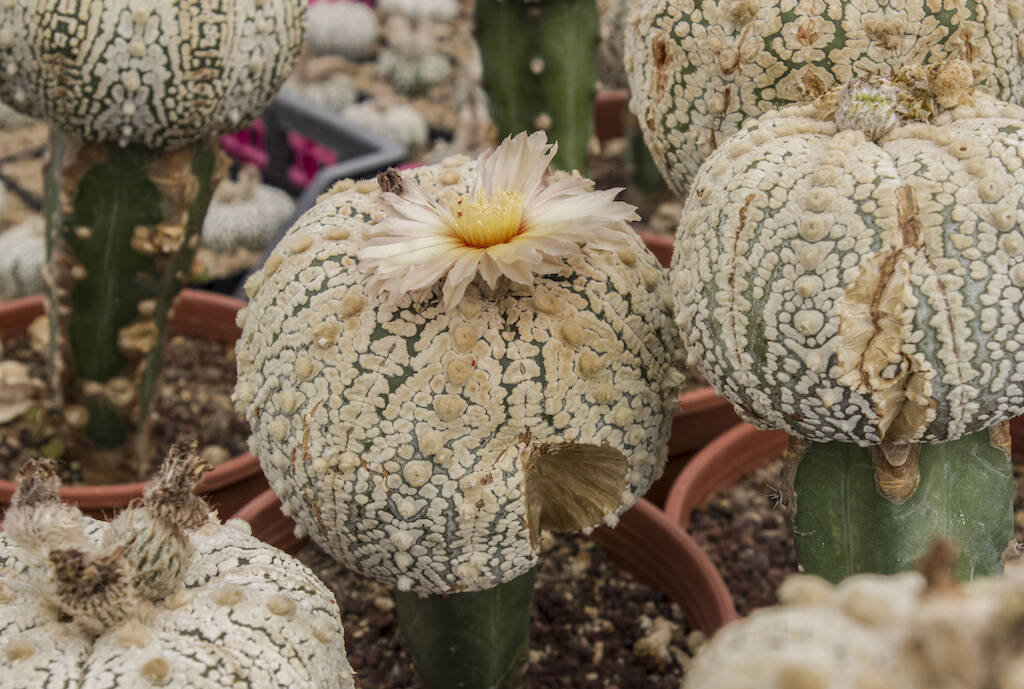
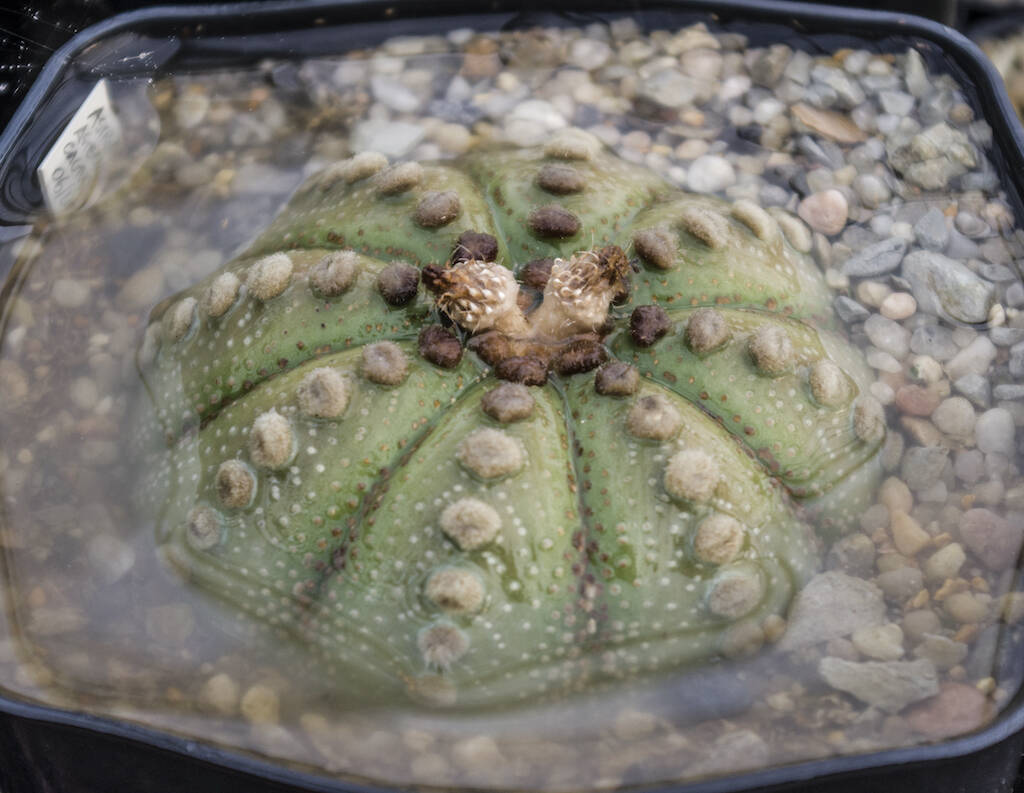
Spring is the season of recovery for all plants, and succulents are no exception. Many species are already in full bloom, such as Stenocactus, Strombocactus, many Turbinicarpus and several Mammillaria. Be careful, however, there is a difference between flowering and vegetative growth: a plant can flower even if it has not fully resumed vegetating. Simply, this is its flowering period and the plant respects it even if it is still coming out of the winter “dormancy” state. As regards temperatures, obviously there is a big difference based on the area in which it is grown, so in some regions of the South the night-time minimums can already be above 10 degrees, while in the North we still have relatively low values, around 2 or 3 degrees. This factor is fundamental to understanding whether we can move our plants outside or not. Equally important is the time to resume watering. Can we start watering cacti and succulents these days or is it better to wait a little longer? Finally: with the start of the summer, is it necessary to carry out some treatments with plant protection products or can this practice be avoided?
Let’s see everything in detail in the following article, so as to move correctly and avoid problems or rot damaging the plants. (…)