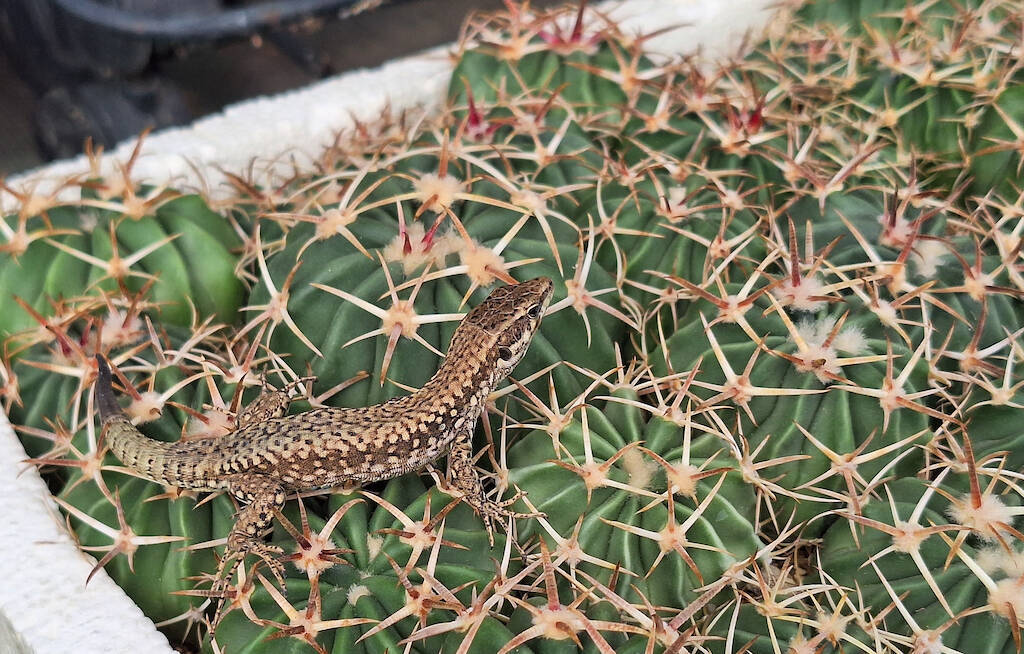
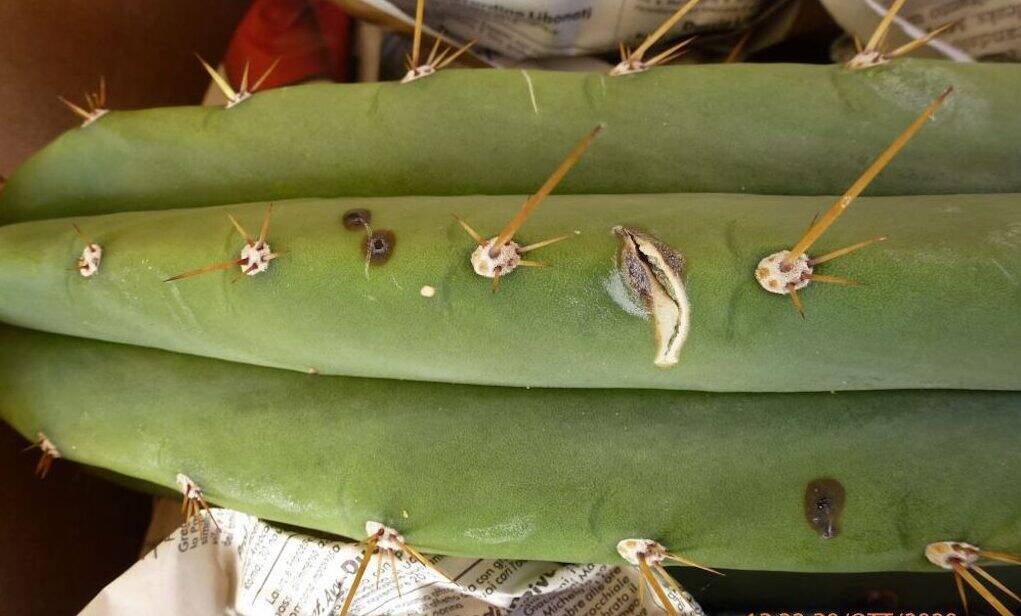
Even a young bat, entangled, poor him, among the deadly hooked thorns of an Ancistrocactus and died in that unwelcome embrace during the night, without my being able to notice it or do anything to free it. In many years of cultivation this has also happened to me as you will see in the photo in the article. Those who grow cacti, especially if they have a greenhouse (although singular encounters can also be had when growing them in a garden, on a terrace or on a balcony) know well that not only insects, but also many reptiles or small mammals usually slip through one plant and another. Lizards, spiders, ants, snails, mantises, small birds and mice (not so much the small ones, the so-called field mice, but the real rats, which devour any plant, thorns or no thorns) abound especially if you grow in countryside, where it is not uncommon to come across some harmless water snakes. They are abundant, in particular, if you prefer spartan cultivation, with reduced use of chemical products. Most of these “guests” do not cause any harm to the plants; still others are useful in the fight against parasites: think of ladybugs or of that little red spider visible to the naked eye that goes for a walk on the stems of cacti and which at first glance causes a stroke, but is actually a useful predator of the very harmful red spider, invisible to the naked eye (unlike the damage it causes to plants).
In this article here is an overview of the encounters with animals or insects that I have had in years of cultivation, both on a small balcony and in the current large greenhouse in the countryside. Above all, here is some useful information to understand which animals or insects are “friends” and which animals or insects are “enemy” and how to keep them at bay. (…)
Per proseguire nella lettura dell'articolo Accedi o Abbonati
To continue reading the article LogIn or Subscribe